Fat loss is primarily governed by energy balance—consuming fewer calories than you burn. However, the quality of the foods you eat plays a crucial role in metabolism, satiety, and hormonal responses. Certain foods enhance fat burning by increasing thermogenesis, reducing appetite, or improving metabolic function. Conversely, some foods slow down fat loss by promoting fat storage, causing insulin spikes, or leading to excessive calorie consumption.
10 Foods That Accelerate Fat Loss
1. Lean Protein Sources
Lean proteins like chicken breast, turkey, fish, and eggs help accelerate fat loss by increasing thermogenesis and preserving lean muscle mass. A study by Pesta and Samuelson (2014) found that high-protein diets increase metabolism and improve satiety, reducing overall caloric intake.
2. Green Tea

Green tea contains catechins and caffeine, which enhance thermogenesis and fat oxidation. A meta-analysis by Hursel et al. (2011) concluded that green tea catechins significantly contribute to weight loss and fat oxidation when combined with a calorie-controlled diet.
3. Chilli Peppers
Capsaicin, the active compound in chilli peppers, has been shown to increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation. Research by Ludy et al. (2012) indicates that capsaicin consumption enhances metabolism and reduces appetite.
4. Whole Grains
Whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats promote fat loss by improving digestion and providing sustained energy. A study by Karl et al. (2017) demonstrated that replacing refined grains with whole grains increases resting metabolic rate and enhances calorie burning.
5. Leafy Greens
Vegetables like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are low in calories but high in fibre, keeping you full for longer. The high micronutrient content in these greens also supports metabolic function (Slavin & Lloyd, 2012).
6. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds contain healthy fats, fibre, and protein, all of which aid in fat loss. Research by Wien et al. (2003) found that almonds enhance weight loss due to their appetite-suppressing effects and impact on metabolism.
7. Greek Yoghurt
Greek yoghurt is rich in protein and probiotics, which aid digestion and increase satiety. A study by Zemel et al. (2004) found that dairy consumption, particularly yoghurt, supports fat loss by enhancing calcium-regulated fat metabolism.
8. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels and suppress appetite. A study by Kondo et al. (2009) revealed that daily ACV consumption leads to significant reductions in body weight and fat mass over time.
9. Fatty Fish
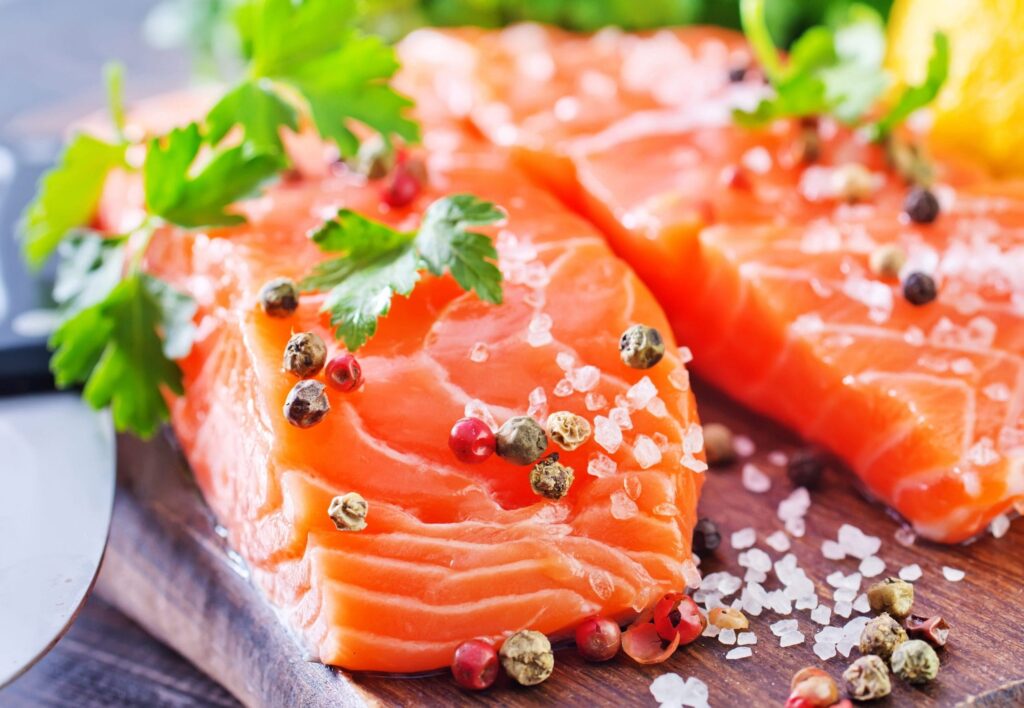

Salmon, mackerel, and sardines contain omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to increased fat oxidation and improved insulin sensitivity. A study by Couet et al. (1997) found that fish oil supplementation leads to greater fat loss.
10. Legumes and Beans
Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are high in protein and fibre, both of which promote satiety and regulate blood sugar levels. A meta-analysis by Kim et al. (2016) confirmed that regular legume consumption is associated with improved weight management and fat loss.
5 Foods That Slow Down Fat Loss
1. Sugary Drinks
Beverages like sodas, fruit juices, and energy drinks contribute to fat gain due to their high sugar content and lack of satiety. A study by Malik et al. (2010) found that sugary drink consumption is directly linked to increased obesity rates.
2. Processed Carbohydrates
White bread, pasta, and pastries cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, leading to fat storage. A study by Ludwig et al. (1999) found that diets high in refined carbohydrates promote increased hunger and fat accumulation.
3. Trans Fats
Partially hydrogenated oils found in fast food and baked goods have been shown to promote inflammation and fat storage. Research by Kavanagh et al. (2007) confirmed that trans fats significantly increase visceral fat deposition.
4. Alcohol

Excessive alcohol consumption impairs fat oxidation and promotes fat storage. A study by Yeomans (2010) found that alcohol reduces metabolic efficiency and increases overall calorie intake by lowering inhibitions regarding food choices.
5. Artificial Sweeteners
Despite being low in calories, artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose can disrupt gut bacteria and lead to metabolic dysfunction. Suez et al. (2014) found that artificial sweeteners can induce glucose intolerance and contribute to weight gain.
Key Takeaways
| Food Category | Effect on Fat Loss |
|---|---|
| Lean protein sources | Enhances thermogenesis, preserves muscle mass |
| Green tea | Boosts metabolism and fat oxidation |
| Chilli peppers | Increases energy expenditure and reduces appetite |
| Whole grains | Improves digestion and increases calorie burning |
| Leafy greens | Low in calories, high in fibre and nutrients |
| Nuts and seeds | Promotes satiety and regulates metabolism |
| Greek yoghurt | High in protein and probiotics for fat metabolism |
| Apple cider vinegar | Regulates blood sugar and suppresses appetite |
| Fatty fish | Supports fat oxidation and improves insulin sensitivity |
| Legumes and beans | High in fibre and protein, supports weight management |
| Sugary drinks | Leads to fat gain due to high sugar content |
| Processed carbohydrates | Causes rapid blood sugar spikes and fat storage |
| Trans fats | Promotes inflammation and visceral fat accumulation |
| Alcohol | Impairs fat oxidation and increases calorie intake |
| Artificial sweeteners | Disrupts metabolism and gut health |
Bibliography
- Couet, C., et al. (1997). ‘Effects of dietary fish oil on body fat mass and basal fat oxidation in healthy adults.’ International Journal of Obesity, 21(8), pp.637-643.
- Hursel, R., et al. (2011). ‘Thermogenic ingredients and body weight regulation.’ International Journal of Obesity, 35(5), pp.661-673.
- Kavanagh, K., et al. (2007). ‘Trans fat diet induces abdominal obesity and changes in insulin sensitivity.’ Obesity, 15(6), pp.1675-1684.
- Kim, S., et al. (2016). ‘Dietary legumes consumption and risk of obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.’ Nutrients, 8(11), p.754.
- Kondo, T., et al. (2009). ‘Vinegar intake reduces body weight, body fat mass, and serum triglyceride levels in obese subjects.’ Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 73(8), pp.1837-1843.
- Malik, V.S., et al. (2010). ‘Sugar-sweetened beverages and weight gain in children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.’ The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 92(4), pp.834-841.
- Slavin, J.L. and Lloyd, B. (2012). ‘Health benefits of fruits and vegetables.’ Advances in Nutrition, 3(4), pp.506-516.
- Suez, J., et al. (2014). ‘Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota.’ Nature, 514(7521), pp.181-186.
- Wien, M., et al. (2003). ‘Almond consumption and weight loss.’ International Journal of Obesity, 27(11), pp.1365-1372.
image sources
- salmon: tycoon
- Annie Thorisdottir post wod: Courtesy of CrossFit Inc.














