In an era where advancements in healthcare and technology are constantly expanding our understanding of human biology, the quest for longevity remains a central focus for many individuals.
Living longer, healthier lives is a universal aspiration, driving both scientific research and personal lifestyle choices. As we strive to unlock the secrets of aging and extend our lifespans, one critical aspect emerges as a cornerstone of this endeavor: diet.
The connection between diet and longevity is not a new concept. Throughout history, cultures around the world have recognized the importance of food in promoting health and longevity. From ancient civilizations to modern scientific studies, there is a growing body of evidence highlighting the profound impact of dietary choices on the aging process and overall well-being.

Today, as we navigate an abundance of dietary options and face an increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the significance of our food choices cannot be overstated. It’s not just about satisfying hunger; it’s about nourishing our bodies with the essential nutrients they need to thrive and flourish for years to come.
In this article, we delve into the realm of longevity foods—nutrient-rich staples that have been shown to support healthspan and potentially extend lifespan. From vibrant fruits to hearty grains, we’ll explore the science behind these dietary powerhouses and uncover the top nine foods you should incorporate into your diet if you’re aiming for a longer, healthier life. Join us on this journey as we unlock the secrets to longevity through the transformative power of food.
Why Food Matters: Exploring the Link Between Diet and Longevity
Food is more than just fuel for our bodies; it’s a fundamental determinant of health and longevity. The saying “you are what you eat” holds a profound truth when it comes to understanding the impact of diet on our overall well-being.
In recent decades, scientific research has increasingly highlighted the intricate relationship between dietary patterns and the aging process, shedding light on how our food choices can influence not only how long we live but also how well we live.

At the core of this connection lies the concept of nutritional quality. The foods we consume provide the building blocks for every physiological process in our bodies, from cellular repair and energy production to immune function and cognitive health.
A diet rich in essential nutrients not only sustains these processes but also helps to protect against the cumulative damage caused by aging and environmental stressors.
Conversely, poor dietary habits characterized by excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats can accelerate aging and increase the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer.
The detrimental effects of such diets are further compounded by lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior, smoking, and stress, creating a perfect storm for premature aging and decreased longevity.
Moreover, emerging research has highlighted the role of diet in shaping the composition and function of the gut microbiota, the vast ecosystem of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract. The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in regulating immune function, metabolism, and inflammation, all of which are key determinants of aging and longevity. By nourishing our bodies with a diverse array of plant-based foods rich in fiber, prebiotics, and phytonutrients, we can support a healthy gut microbiome and promote longevity from the inside out.
Beyond the physiological effects, food also holds cultural, social, and emotional significance that can profoundly impact our relationship with eating and overall well-being. Sharing meals with loved ones, savoring the flavors of seasonal ingredients, and embracing culinary traditions can enhance not only the nutritional value of our diets but also our overall quality of life.
In light of these insights, it becomes evident that food matters far beyond its caloric content or macronutrient composition.
It serves as a potent tool for promoting health, vitality, and longevity, offering a pathway towards a more vibrant and fulfilling life. As we continue to unravel the complex interplay between diet and aging, one thing remains clear: the choices we make at the dinner table today can shape our healthspan and longevity for years to come.
Key Nutrients for Longevity: A Comprehensive Overview
When it comes to promoting longevity and optimal health, the importance of consuming a nutrient-rich diet cannot be overstated.
Certain key nutrients play essential roles in supporting various physiological processes, protecting against age-related decline, and fostering resilience against chronic diseases. In this comprehensive overview, we explore the critical nutrients that have been linked to longevity and delve into their respective benefits for overall well-being.
Antioxidants:
Antioxidants are compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, thereby reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Key antioxidant nutrients include vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, and flavonoids found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
By scavenging free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage, antioxidants may help slow down the aging process and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are essential fats found primarily in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
These fatty acids play crucial roles in brain health, cardiovascular function, and inflammation regulation.

Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of heart disease, improve cognitive function, and promote healthy aging by supporting brain structure and function.
Fiber:
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate found in plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
Dietary fiber provides numerous health benefits, including promoting digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and lowering cholesterol.
By supporting a healthy gut microbiome and facilitating regular bowel movements, fiber may reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and colorectal cancer.
Vitamins and Minerals:
Essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, calcium, magnesium, and potassium, are vital for maintaining overall health and vitality.
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in bone health, immune function, and mood regulation, while vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function and red blood cell production.
Calcium, magnesium, and potassium are important for bone strength, muscle function, and electrolyte balance, respectively.
Obtaining adequate amounts of these vitamins and minerals through a balanced diet or supplementation may support longevity and reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
Phytonutrients:
Phytonutrients are bioactive compounds found in plant foods that possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties.
Examples of phytonutrients include polyphenols, carotenoids, and flavonoids, which are abundant in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices.
Research suggests that phytonutrients may play a role in preventing chronic diseases, protecting against age-related cognitive decline, and promoting longevity through their diverse health-promoting effects.
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients into your diet can provide a solid foundation for supporting longevity and overall well-being.
By nourishing your body with these essential nutrients, you can optimize your healthspan and enhance your quality of life as you age.
1. Blueberries: Tiny Fruit, Big Benefits
Blueberries are more than just a delicious addition to your morning oatmeal or smoothie bowl; they are nutritional powerhouses packed with an impressive array of health-promoting compounds.
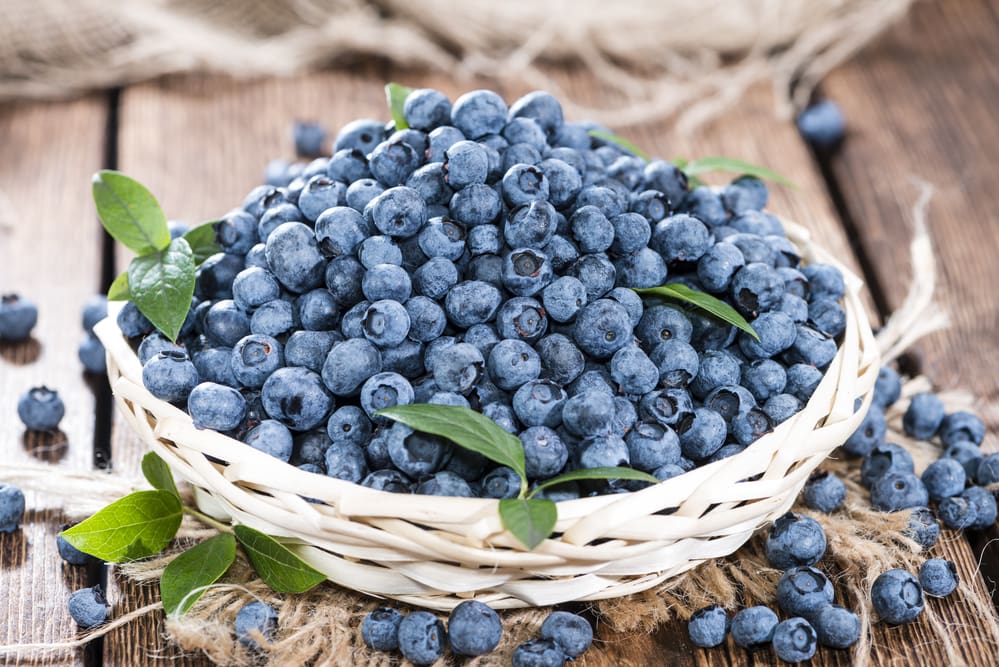

These small, vibrant berries belong to the Vaccinium genus and are renowned for their rich flavor and numerous health benefits. In this article, we explore the science behind blueberries and uncover the compelling reasons to include them in your diet for enhanced well-being and longevity.
Nutrient Profile:
Despite their small size, blueberries are loaded with essential nutrients, including vitamins C and K, manganese, and dietary fiber.
One cup (148 grams) of fresh blueberries provides approximately 24% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C, which supports immune function and collagen synthesis.
Blueberries are also rich in antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which give them their distinctive blue-purple hue and contribute to their health-promoting properties.
Antioxidant Power:
Blueberries are renowned for their high antioxidant content, which helps protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
Anthocyanins, the pigments responsible for the berry’s vibrant color, are potent antioxidants that have been linked to numerous health benefits, including reduced inflammation, improved cognitive function, and enhanced cardiovascular health.
Research suggests that regular consumption of blueberries may help lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and age-related cognitive decline.
Heart Health:
Several studies have highlighted the cardiovascular benefits of blueberries, including their ability to lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
The antioxidants found in blueberries may help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are implicated in the development of cardiovascular disorders.
Incorporating blueberries into your diet as part of a heart-healthy eating pattern may contribute to better cardiovascular outcomes and overall heart health.
Brain Function:
Emerging research suggests that blueberries may have positive effects on brain health and cognitive function, particularly in older adults.
Anthocyanins and other bioactive compounds found in blueberries have been shown to support neuronal communication, protect against age-related cognitive decline, and enhance memory and learning abilities.

Regular consumption of blueberries, either fresh or frozen, may help preserve brain function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
How to Enjoy Blueberries:
Blueberries are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in various ways, including fresh, frozen, dried, or as a juice or puree.
Add fresh blueberries to breakfast cereals, yogurt, salads, or smoothies for a nutritious boost of flavor and antioxidants.
Incorporate frozen blueberries into baked goods, pancakes, or muffins for a convenient and tasty addition to your meals and snacks.
Consider including blueberry-based sauces, jams, or dressings in your culinary repertoire to elevate the nutritional profile of your favorite dishes.
In conclusion, blueberries are not only delicious but also offer a myriad of health benefits that make them a valuable addition to any diet.
Whether you enjoy them as a snack, a topping, or an ingredient in your favorite recipes, incorporating blueberries into your daily routine can support heart health, brain function, and overall well-being. So go ahead and indulge in these tiny fruits with big benefits, and savor the taste of vitality and longevity with every bite.
2. Leafy Greens: Powerhouses of Nutrients
Leafy greens are among the most nutrient-dense foods available, boasting an impressive array of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients.
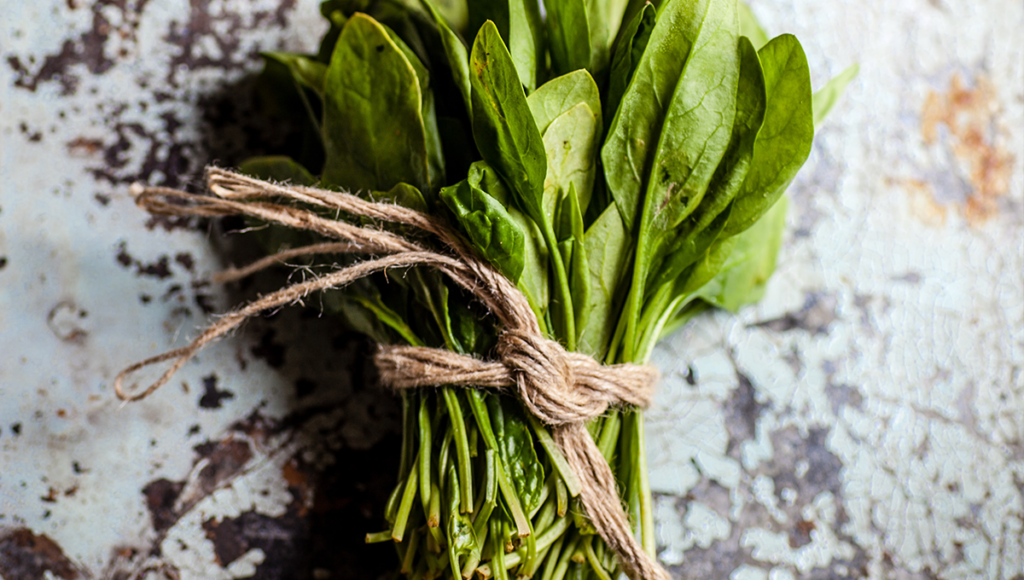

From kale and spinach to arugula and Swiss chard, these vibrant green vegetables are not only delicious but also offer numerous health benefits. In this article, we delve into the nutritional profile of leafy greens and explore the compelling reasons to incorporate them into your diet for optimal health and longevity.
Nutrient Density:
Leafy greens are low in calories but high in essential nutrients, making them a nutrient-dense addition to any diet.
They are particularly rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
These vitamins and minerals play critical roles in supporting immune function, bone health, blood clotting, and electrolyte balance.
Antioxidant Content:
Leafy greens are packed with antioxidants, including carotenoids (such as beta-carotene and lutein), flavonoids, and vitamin C.
Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and protecting against chronic diseases.
Regular consumption of leafy greens may lower the risk of heart disease, certain cancers, and age-related conditions such as macular degeneration.
Fiber-Rich:
Leafy greens are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which promotes digestive health, regulates blood sugar levels, and supports weight management.
Fiber adds bulk to the diet, aiding in satiety and promoting feelings of fullness, which can help prevent overeating and support healthy weight loss.
Including a variety of leafy greens in your meals can contribute to a well-rounded, fiber-rich diet that supports overall health and well-being.
Versatility and Culinary Uses:
Leafy greens are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in a variety of ways, including raw, cooked, or blended into smoothies and juices.
Add spinach or kale to salads, sandwiches, wraps, and omelets for an extra dose of nutrients and flavor.
Incorporate leafy greens into soups, stews, stir-fries, and pasta dishes for a boost of color, texture, and nutrition.
Blend leafy greens into green smoothies or juices with fruits, vegetables, and herbs for a refreshing and nutrient-packed beverage.
Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly:
Leafy greens are among the most environmentally sustainable crops, requiring relatively low water and land resources compared to animal-based foods.
Choosing to include more leafy greens in your diet can help reduce your carbon footprint and support sustainable food systems.
By opting for locally grown, organic leafy greens whenever possible, you can further minimize environmental impact and promote eco-friendly eating habits.
In conclusion, leafy greens are nutritional powerhouses that offer a wide range of health benefits and culinary possibilities. Whether you prefer spinach, kale, collard greens, or any other variety, incorporating leafy greens into your diet can enhance your overall health, vitality, and longevity. So next time you’re planning your meals, remember to make leafy greens a staple part of your plate and savor the taste of wellness with every bite.
3. Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Rich Delights
Fatty fish are not only a delicious addition to your plate but also a nutritional powerhouse, particularly when it comes to omega-3 fatty acids.
These essential fats are renowned for their numerous health benefits, ranging from supporting heart health to promoting brain function and reducing inflammation. In this article, we explore the nutritional benefits of fatty fish and why they should be a regular part of your diet for optimal health and longevity.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, and herring are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Omega-3 fatty acids play crucial roles in supporting cardiovascular health, brain function, and inflammatory response regulation.
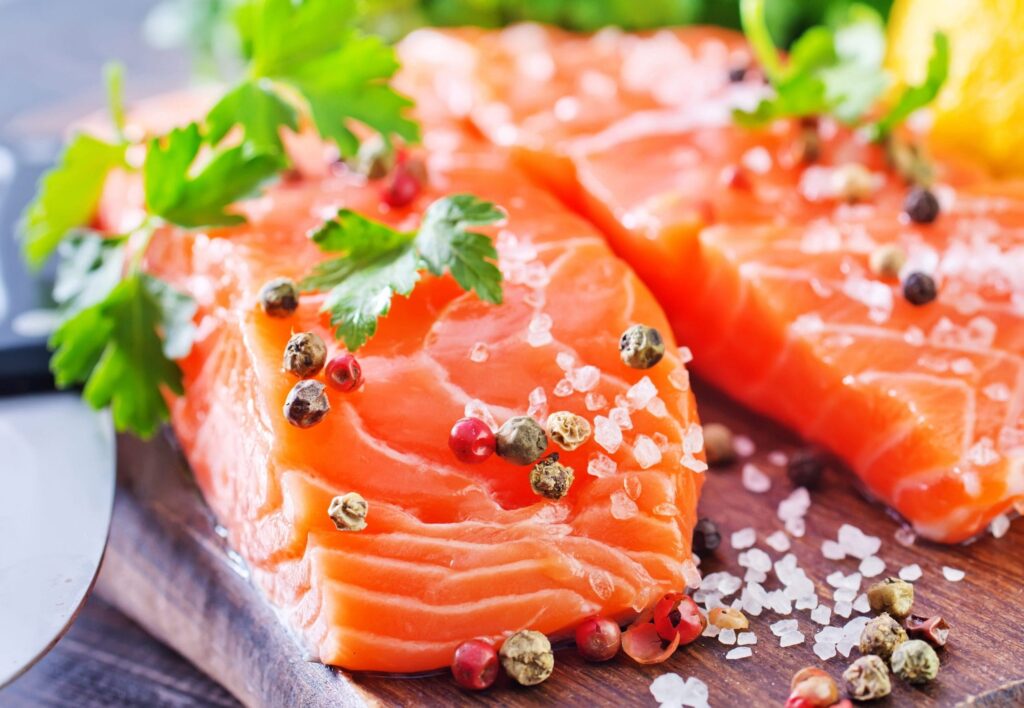

Research suggests that regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and decrease inflammation throughout the body.
Heart Health Benefits:
Fatty fish are often touted as heart-healthy foods due to their high omega-3 content and associated cardiovascular benefits.
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce triglyceride levels, decrease blood clot formation, and improve arterial function, all of which contribute to a lower risk of heart disease.
Incorporating fatty fish into your diet as part of a balanced eating pattern may help protect against heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications.
Brain Function and Cognitive Health:
DHA, one of the primary omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, is a major component of brain cell membranes and plays a crucial role in cognitive function and development.
Studies have suggested that adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly during early life and aging, may support brain health, improve memory, and reduce the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Including fatty fish in your diet on a regular basis may help maintain cognitive function and promote optimal brain health throughout the lifespan.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
Omega-3 fatty acids possess potent anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body and mitigate the risk of chronic diseases associated with excessive inflammation.
Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and certain cancers.
By incorporating omega-3-rich fatty fish into your diet, you can help modulate inflammation and promote overall health and well-being.
How to Enjoy Fatty Fish:
Fatty fish can be enjoyed in a variety of delicious ways, including grilled, baked, broiled, or pan-seared.
Experiment with different seasoning blends, marinades, and sauces to enhance the flavor of fatty fish while keeping preparations simple and nutritious.
Include fatty fish in salads, sandwiches, wraps, tacos, and sushi rolls for a tasty and nutritious meal option.
Opt for wild-caught fatty fish whenever possible to ensure the highest quality and sustainability.
In conclusion, fatty fish are omega-3 rich delights that offer an array of health benefits, ranging from supporting heart health and brain function to reducing inflammation throughout the body. By incorporating fatty fish into your diet on a regular basis, you can nourish your body with essential nutrients and promote overall health, vitality, and longevity.
So go ahead and indulge in the flavorful goodness of fatty fish, and reap the rewards of their nutritional bounty with every bite.
4. Nuts and Seeds: Crunchy Packages of Health
Nuts and seeds are nature’s crunchy treasures, prized not only for their delicious taste and satisfying crunch but also for their impressive nutritional profile. Packed with essential nutrients, healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, nuts and seeds offer a wide range of health benefits that make them a valuable addition to any diet.

In this article, we explore the myriad health benefits of nuts and seeds and why they should be a regular part of your eating routine for optimal health and longevity.
Heart Health:
Nuts and seeds are rich in heart-healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which have been shown to improve cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of heart disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in certain nuts and seeds such as walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, play a crucial role in supporting cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Regular consumption of nuts and seeds as part of a balanced diet may help lower blood pressure, improve blood vessel function, and protect against heart disease.
Nutrient Density:
Despite their small size, nuts and seeds are nutrient powerhouses, packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall health and well-being.
They are excellent sources of vitamin E, magnesium, potassium, and other essential nutrients that play key roles in supporting immune function, bone health, muscle function, and nerve signaling.
Incorporating a variety of nuts and seeds into your diet can help ensure that you meet your daily nutrient needs and maintain optimal health.
Weight Management:
Contrary to popular belief, nuts and seeds can be beneficial for weight management when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Their combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber helps promote feelings of fullness and satiety, which can help prevent overeating and support weight loss or weight maintenance efforts.

Studies have shown that individuals who include nuts and seeds in their diet tend to have lower body weight, reduced waist circumference, and a lower risk of obesity compared to those who consume them infrequently or not at all.
Blood Sugar Control:
Nuts and seeds have a low glycemic index, meaning they cause a slower and more gradual increase in blood sugar levels compared to high-glycemic foods.
The fiber and protein found in nuts and seeds further help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent spikes and crashes in energy levels.
Including nuts and seeds in meals and snacks can help regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
How to Enjoy Nuts and Seeds:
Nuts and seeds can be enjoyed in a variety of ways, including raw, roasted, toasted, or as nut butters and seed spreads.
Sprinkle nuts and seeds over salads, yogurt, oatmeal, or smoothie bowls for added texture, flavor, and nutrition.
Incorporate nuts and seeds into baked goods, granola bars, energy balls, and trail mixes for a convenient and portable snack option.
Experiment with different nut and seed varieties, such as almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds, to discover your favorites and diversify your nutrient intake.
In conclusion, nuts and seeds are crunchy packages of health that offer a wide range of nutritional benefits, including supporting heart health, weight management, blood sugar control, and overall well-being. By including a variety of nuts and seeds in your diet on a regular basis, you can nourish your body with essential nutrients and promote optimal health, vitality, and longevity. So go ahead and indulge in the wholesome goodness of nuts and seeds, and enjoy the taste of health with every satisfying crunch.
5. Whole Grains: Fiber-Rich Staples for Longevity
Whole grains are a cornerstone of a healthy diet, prized for their rich fiber content, essential nutrients, and numerous health benefits.
Unlike refined grains, which have been stripped of their bran and germ during processing, whole grains retain all parts of the grain, including the fiber-rich outer layer.
In this article, we explore the nutritional benefits of whole grains and why they should be a staple part of your diet for longevity and overall well-being.
Fiber Content:
Whole grains are renowned for their high fiber content, which plays a crucial role in supporting digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and promoting satiety.
Dietary fiber adds bulk to the stool, preventing constipation and promoting regularity, which is essential for optimal digestive function and gut health.

Consuming fiber-rich whole grains has been linked to a reduced risk of digestive disorders such as diverticulosis, hemorrhoids, and colorectal cancer.
Nutrient Density:
Whole grains are rich sources of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients.
They provide a wide range of vitamins and minerals such as B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folate), iron, magnesium, zinc, and selenium, which are vital for energy production, immune function, and overall health.
The antioxidants found in whole grains help protect cells from oxidative damage, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Heart Health Benefits:
Whole grains have been shown to support heart health by reducing cholesterol levels, lowering blood pressure, and improving blood vessel function.
The soluble fiber found in whole grains helps lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive tract and removing it from the body.
Regular consumption of whole grains may help lower the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications by improving lipid profiles and reducing inflammation.
Weight Management:
Whole grains can be beneficial for weight management due to their high fiber content and low glycemic index, which helps promote feelings of fullness and satiety.
Including whole grains in meals and snacks can help prevent overeating, reduce calorie intake, and support weight loss or weight maintenance efforts.
Studies have shown that individuals who consume more whole grains tend to have lower body weight, smaller waist circumference, and a reduced risk of obesity compared to those who consume fewer whole grains.
How to Enjoy Whole Grains:
There are numerous delicious ways to incorporate whole grains into your diet, from breakfast to dinner and everything in between.
Start your day with whole grain cereals, oatmeal, or whole grain toast topped with nut butter and fruit for a nutritious and satisfying breakfast.
Swap refined grains for whole grains in recipes such as soups, salads, stir-fries, casseroles, and side dishes to boost the fiber and nutrient content of your meals.
Experiment with a variety of whole grains, including brown rice, quinoa, barley, farro, bulgur, and whole wheat pasta, to discover new flavors and textures.
In conclusion, whole grains are fiber-rich staples that offer a multitude of health benefits, including supporting digestive health, heart health, weight management, and overall well-being. By incorporating a variety of whole grains into your diet on a regular basis, you can nourish your body with essential nutrients and promote longevity and vitality. So make whole grains a central part of your meals and enjoy the taste of health with every wholesome bite.
6. Legumes: Plant-Based Protein for a Longer Life
Legumes, encompassing a diverse group of plant foods such as beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas, are nutritional powerhouses celebrated for their high protein content, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients.
As one of the cornerstones of plant-based diets worldwide, legumes offer a multitude of health benefits that make them an essential component of a balanced and nutritious eating pattern.
In this article, we explore the nutritional benefits of legumes and why they are a valuable addition to your diet for longevity and overall well-being.
Plant-Based Protein:
Legumes are rich sources of plant-based protein, making them an excellent alternative to animal protein for individuals following vegetarian, vegan, or flexitarian diets.
They provide a complete or complementary source of protein when paired with grains, nuts, or seeds, offering all essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance.
Including legumes in meals and snacks can help meet daily protein requirements, support muscle health, and promote satiety and weight management.
Fiber-Rich:
Legumes are renowned for their high fiber content, particularly soluble fiber, which plays a crucial role in supporting digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and lowering cholesterol.
Dietary fiber adds bulk to the stool, promoting regularity and preventing constipation, while also slowing down the absorption of glucose and cholesterol in the bloodstream.
Regular consumption of legumes has been associated with a reduced risk of digestive disorders, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
Nutrient Density:
Legumes are packed with essential nutrients, including vitamins (such as folate, vitamin B6, and vitamin K), minerals (such as iron, magnesium, potassium, and zinc), and antioxidants (such as flavonoids and polyphenols).
They provide a wide range of micronutrients that support various physiological processes in the body, including energy production, immune function, bone health, and antioxidant defense.
Heart Health Benefits:
Legumes have been shown to support heart health by lowering cholesterol levels, reducing blood pressure, and improving blood vessel function.

The soluble fiber and phytonutrients found in legumes help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, decrease inflammation, and promote endothelial function, all of which contribute to a lower risk of heart disease.
Including legumes in your diet as part of a heart-healthy eating pattern may help prevent heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications.
How to Enjoy Legumes:
There are countless delicious ways to incorporate legumes into your diet, from soups and stews to salads, wraps, and dips.
Experiment with different varieties of legumes, including black beans, kidney beans, chickpeas, lentils, and peas, to discover new flavors and textures.
Use legumes as a meat substitute in traditional recipes such as chili, tacos, burgers, and pasta dishes to boost the protein and fiber content of your meals.
Incorporate legumes into side dishes, casseroles, and grain bowls for a nutritious and satisfying addition to your plate.
In conclusion, legumes are plant-based protein powerhouses that offer a wealth of health benefits, including supporting muscle health, digestive health, heart health, and overall well-being. By including a variety of legumes in your diet on a regular basis, you can nourish your body with essential nutrients and promote longevity and vitality.
So embrace the versatility and nutritional goodness of legumes, and enjoy the taste of health with every satisfying bite.
7. Olive Oil: Liquid Gold for Heart Health
Olive oil, often referred to as “liquid gold,” has been treasured for centuries for its rich flavor, versatility in cooking, and numerous health benefits.
Derived from the fruit of the olive tree (Olea europaea), olive oil is a staple of the Mediterranean diet—a dietary pattern celebrated for its association with longevity and reduced risk of chronic diseases. In this article, we explore the remarkable health benefits of olive oil, particularly its role in supporting heart health and overall well-being.
Heart-Healthy Fats:
Olive oil is predominantly composed of monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which have been shown to improve heart health by lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Monounsaturated fats help increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels, improve blood vessel function, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to a healthier heart and reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Antioxidant Properties:
Extra virgin olive oil, in particular, is rich in antioxidants such as polyphenols, tocopherols (vitamin E), and carotenoids, which help protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
The polyphenols found in olive oil have potent anti-inflammatory and antiatherogenic effects, helping to prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the development of heart disease, as well as other chronic conditions such as diabetes, arthritis, and cancer.
Olive oil has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects, reducing levels of inflammatory markers and cytokines in the body and promoting overall health and well-being.
Blood Pressure Regulation:
Consuming olive oil as part of a balanced diet has been associated with lower blood pressure levels, which is important for maintaining cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of hypertension.
The polyphenols and monounsaturated fats in olive oil help improve endothelial function, relax blood vessels, and promote healthy blood flow, contributing to lower blood pressure and improved vascular health.
How to Incorporate Olive Oil into Your Diet:
Use extra virgin olive oil as a primary cooking oil for sautéing, roasting, grilling, and baking, as it has a high smoke point and retains its flavor and nutritional properties at high temperatures.
Drizzle olive oil over salads, vegetables, pasta, and bread for added flavor and richness.
Use olive oil as a base for homemade salad dressings, marinades, and dips, combining it with herbs, spices, and vinegar or lemon juice for a delicious and nutritious condiment.
In conclusion, olive oil is indeed liquid gold when it comes to promoting heart health and overall well-being. By incorporating olive oil into your diet on a regular basis, you can enjoy its rich flavor and reap the numerous health benefits it offers, including reduced risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, and decreased inflammation. So embrace olive oil as a culinary staple and savor the taste of vitality and longevity with every drizzle.
8. Berries: Colorful Gems of Antioxidants
Berries, with their vibrant hues and irresistible sweetness, are not only a delightful addition to meals and snacks but also nutritional powerhouses packed with antioxidants and essential nutrients.
From strawberries and blueberries to raspberries and blackberries, these tiny fruits offer a wide range of health benefits that make them a valuable component of a balanced diet.
In this article, we explore the remarkable health benefits of berries, particularly their antioxidant properties and their potential to promote overall well-being and longevity.
Antioxidant Richness:
Berries are among the richest dietary sources of antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, flavonoids, polyphenols, and anthocyanins.
Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and protecting against chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
The vibrant colors of berries, particularly blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are indicative of their high antioxidant content, with darker berries generally containing higher levels of anthocyanins and other phytonutrients.
Heart Health Benefits:
Numerous studies have shown that regular consumption of berries is associated with improved heart health and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
The antioxidants and polyphenols found in berries help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, improve blood vessel function, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to a healthier heart and reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Incorporating berries into your diet as part of a heart-healthy eating pattern may help lower blood pressure, improve lipid profiles, and protect against atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular complications.
Brain Function and Cognitive Health:
Berries have been shown to support brain health and cognitive function, particularly in aging adults.
The antioxidants and phytonutrients found in berries help protect brain cells from oxidative damage, reduce inflammation in the brain, and enhance neuronal communication and signaling.
Regular consumption of berries, particularly blueberries, has been linked to improvements in memory, learning, and cognitive performance, as well as a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Anti-Cancer Properties:
Some studies suggest that berries may have anti-cancer properties, potentially reducing the risk of certain types of cancer due to their high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory content.
The antioxidants found in berries help neutralize carcinogens, inhibit the growth of cancer cells, and promote apoptosis (cell death) in cancerous cells, reducing the risk of tumor formation and progression.
While more research is needed to fully understand the role of berries in cancer prevention and treatment, including them in a balanced diet may offer protective benefits against certain types of cancer.
How to Enjoy Berries:
Berries are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed fresh, frozen, dried, or as juices, jams, and preserves.
Add fresh berries to breakfast cereals, yogurt, oatmeal, pancakes, waffles, or smoothie bowls for a burst of flavor and nutrition.
Incorporate frozen berries into baked goods, desserts, sauces, and fruit salads for a convenient and delicious option year-round.
Enjoy dried berries as a portable snack on their own or mixed with nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate for a tasty and nutritious trail mix.
In conclusion, berries are indeed colorful gems of antioxidants that offer a multitude of health benefits, including supporting heart health, brain function, and overall well-being. By including a variety of berries in your diet on a regular basis, you can nourish your body with essential nutrients and promote longevity and vitality.
So embrace the sweetness and nutritional goodness of berries, and enjoy the taste of health with every juicy bite.
Conclusion: Incorporating Longevity Foods Into Your Lifestyle
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the foods we eat play a crucial role in promoting longevity, vitality, and overall well-being.
From nutrient-dense leafy greens and colorful berries to heart-healthy fatty fish and antioxidant-rich olive oil, incorporating a variety of longevity foods into your diet can have a profound impact on your health and quality of life.
By prioritizing whole, minimally processed foods and emphasizing plant-based options rich in nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants, you can nourish your body from the inside out and support optimal healthspan—the number of years you live in good health and vitality.
Here are some key takeaways to help you incorporate longevity foods into your lifestyle:
Prioritize Plant-Based Foods: Fill your plate with a colorful array of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. These plant-based foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytonutrients that support overall health and longevity.
Choose Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats such as olive oil, fatty fish, nuts, and seeds in your diet. These fats provide essential omega-3 fatty acids, monounsaturated fats, and antioxidants that promote heart health, brain function, and inflammation regulation.
Focus on Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, and whole wheat over refined grains. Whole grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a nutritious foundation for meals and snacks.
Incorporate Lean Protein: Include lean sources of protein such as poultry, fish, tofu, tempeh, legumes, and low-fat dairy in your diet. Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance, as well as satiety and weight management.
Minimize Processed Foods and Added Sugars: Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and sugary beverages, which provide empty calories and contribute to inflammation, weight gain, and chronic diseases.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support optimal bodily functions. Herbal teas, sparkling water, and infused water are also refreshing options.
Practice Mindful Eating: Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, and savor each bite of food mindfully. Pay attention to the flavors, textures, and sensations of eating, and cultivate gratitude for the nourishment your food provides.
Incorporating longevity foods into your lifestyle is not only beneficial for your physical health but also for your mental and emotional well-being.
By making nutritious food choices a priority and adopting a balanced approach to eating, you can lay the foundation for a long, healthy, and fulfilling life. So savor the taste of vitality and embrace the journey toward optimal health and longevity—one delicious bite at a time.
Learn More
5 Reasons Why Walking for 30 Minutes Every Day will Help You Live a Longer Life
13 Easy to Cook Meals for Burning Your Visceral Fat Quicker (GET LEAN FAST)
8 Reasons Why Meal Prepping is Your Golden Ticket to a Flatter Stomach in 2024
Perfect 5 Minutes Posture Routine
How to Hack Muscle Growth in 2024
How to Get Stronger and Better Looking Glutes
The Perfect Biceps Workout for Muscle Mass and Great Looking Arms
image sources
- CrossFit Open high five: Photo courtesy of CrossFit Inc.
- Training-Secrets-for-Masters-athletes: Photo Courtesy of CrossFit Inc
- Masters-Athlete-barbell: Photo Courtesy of CrossFit Inc
- salmon: tycoon
- Cashew nuts and pistacchio: Mehran B on Pexels
- crossfit-games-age-groups: Courtesy of CrossFit Inc.
- Bubba Hagood: Photo courtesy of CrossFit Inc.














