Navigating the diverse landscape of diets can be as confusing as choosing between two equally enticing paths. Some advocate for the elimination of carbohydrates, endorsing ketogenic or even carnivorous diets. Others champion plant-based and vegan diets, urging higher carbohydrate intake while eschewing all animal products. The success of these diets for different individuals underscores the bio-individual nature of nutrition.
This article, based on a video by Dr Anthony Balduzzi, demystifies the complexities and presents the seven universal principles of healthy eating, applicable whether you’re inclined towards keto or a plant-based diet.
Dr. Anthony Balduzzi is a naturopathic doctor, national champion bodybuilder and founder of the Fit Father Project and Fit Mother Project – online health and fitness communities aimed at empowering busy parents to get healthy, lose weight, and build muscle through practical nutrition and exercise plans. The information you will see below was based on a video he shared on his Fit Father Project YouTube channel.
In today’s world, diets have taken on a near-religious fervour, with passionate advocates on all sides. While some extol the virtues of keto and carnivore diets, others vehemently support plant-based regimens. The multitude of choices can be overwhelming, especially when each appears to work well for different individuals. However, there are underlying principles that transcend dietary dogma. Understanding these principles can guide you towards a healthier lifestyle, regardless of specific dietary preferences.
7 Rules of Healthy Eating That Are ALWAYS True
To bridge the divide between different dietary philosophies, it is essential to identify common ground. The seven principles of healthy eating offer a framework that supports optimal health, whether you are following a ketogenic or plant-based diet. These principles provide a holistic approach to nutrition that can help you tailor your eating habits to your unique needs.
Principle 1: Eliminate Processed Sugars
One of the foremost tenets of any healthy diet is the elimination of processed sugars. In the United States, the average person consumes an astounding 152 pounds of sugar annually, which equates to about three pounds per week. This excessive intake is a significant factor in the prevalence of health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.

Processed sugars wreak havoc on the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. When consumed in large amounts, sugar overloads the pancreas, causing it to produce excessive insulin to manage blood sugar levels. Over time, this leads to insulin resistance, weight gain, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Unlike whole foods that naturally contain sugar, processed sugars do not offer the same satiety, leading to overconsumption and poor health outcomes.
Sugar Alternatives: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
Principle 2: Avoid Low-Quality Animal Products
The quality of the animal products you consume is as important as their presence in your diet. There is a stark difference between grass-fed and corn-fed beef, not only in taste but also in nutritional value. Grass-fed beef contains higher levels of healthy fats such as CLA (conjugated linoleic acid) and omega-3 fatty acids, while corn-fed beef has more inflammatory omega-6 fatty acids.
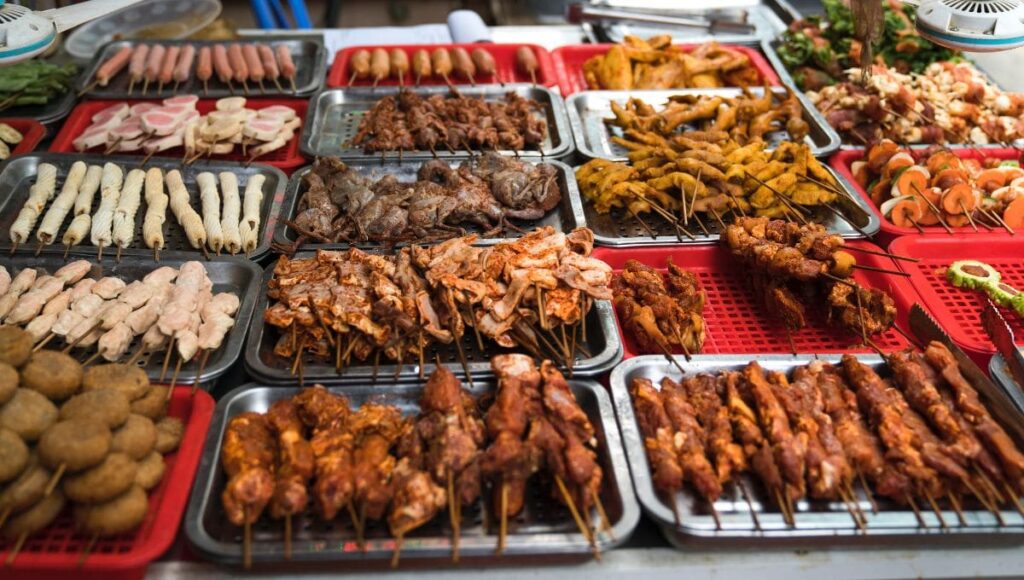

Research links the consumption of low-quality, processed animal products to various health issues, including cancer. These products often contain harmful additives like nitrites, which interact with gut bacteria to form carcinogenic compounds. Therefore, if you choose to include animal products in your diet, prioritize high-quality, organic options to minimize health risks.
Principle 3: Consume a Wide Variety of Organic Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are the cornerstone of a nutritious diet, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients that support overall health. Each colour in the spectrum of fruits and vegetables offers different health benefits. For instance, the proanthocyanidins in blueberries and black rice are powerful antioxidants that protect against oxidative stress.
Eating a diverse array of fruits and vegetables ensures that you receive a broad range of nutrients necessary for various bodily functions. This practice also supports a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for digestion, immune function, and overall well-being.

Principle 4: Support Your Gut Microbiome
Your digestive tract is home to trillions of bacteria that play a pivotal role in your health. These microorganisms help digest food, synthesize vitamins, and protect against harmful pathogens. A diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes a healthy gut microbiome by providing the necessary fuel for beneficial bacteria.
Fermented foods such as yoghurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha are excellent sources of probiotics that enhance gut health. Including these foods in your diet can improve digestion, boost the immune system, and even influence mood and mental health.
Principle 5: Focus on Digestion, Absorption, and Elimination
The nutritional value of your food depends not only on what you eat but also on how well your body can digest, absorb, and eliminate it. Foods that are easily digestible and well-absorbed provide the most benefit. For instance, animal products take longer to digest and can linger in the digestive tract, potentially leading to negative health outcomes if not paired with fibrous vegetables.
Monitoring your digestive health through the quality and regularity of your bowel movements can provide insights into how well your diet is working for you. Incorporating plenty of fibre-rich foods and staying hydrated can aid in efficient digestion and elimination.
Principle 6: Balance Your Energy Intake
Regardless of your dietary preferences, maintaining a balance between your caloric intake and energy expenditure is vital for health. Overeating or undereating can both lead to adverse health effects. It is important to consume the right amount of calories to support your activity level and metabolic needs.
Intermittent fasting and mindful eating practices can help regulate caloric intake without the need for strict calorie counting. Understanding your body’s hunger cues and eating accordingly can promote a healthy weight and prevent metabolic disorders.
Principle 7: Keep It Simple
The best diet is one that is sustainable and enjoyable. Overly complex or restrictive diets are difficult to maintain in the long term. Instead, focus on simple, whole foods that you enjoy and can easily incorporate into your daily routine.
Concepts like the “perfect plate”—dividing your plate into sections for protein, vegetables, and healthy fats or carbs—can simplify meal planning and ensure nutritional balance. The goal is to create a diet that supports your health and fits seamlessly into your lifestyle.

The seven principles of healthy eating provide a comprehensive approach to nutrition that transcends dietary trends. By focusing on these core principles, you can create a balanced, sustainable diet that promotes health and well-being. Whether you lean towards a ketogenic or plant-based diet, these guidelines can help you navigate the complex world of nutrition with confidence and clarity. Remember, the best diet is the one that you can stick to and that makes you feel your best.














