Building muscle isn’t just about hitting the gym; it’s about fuelling your body right. Nutrition plays a critical role in muscle development, so what you eat can either help or hinder your progress. Eating the right foods supports muscle repair, growth, and overall energy, allowing you to get the most out of your workouts. Whether you’re looking to bulk up or simply increase your lean muscle mass, this guide covers the essential nutrients and best foods for muscle gain. From proteins and carbs to healthy fats and supplements, understanding what to eat will make all the difference in achieving your goals.
Key Nutritional Principles for Muscle Gain
Before diving into the specific foods, it’s helpful to understand the foundational principles of muscle-building nutrition.
- Caloric Surplus: To build muscle, you generally need to consume more calories than you burn. Aiming for a moderate surplus ensures that your body has enough energy for muscle synthesis.
- Protein for Muscle Repair: Protein provides amino acids, the building blocks for muscle tissue, and is essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Carbohydrates for Energy: Carbs replenish glycogen stores, providing fuel for workouts and supporting recovery.
- Healthy Fats for Hormone Production: Fats aid in hormone production, including testosterone, which plays a role in muscle growth.
Complete 8-Week Plan to Completely Transform Your Body
High-Quality Protein Sources for Muscle Growth
Protein is the most critical macronutrient for muscle gain. Aim to consume 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day. Protein should ideally be spread across meals to ensure a consistent supply of amino acids to your muscles throughout the day.
Lean Meat and Poultry
- Chicken Breast: High in protein with minimal fat, making it a staple for muscle builders.
- Turkey Breast: Another lean option, turkey is rich in protein and low in saturated fats.
- Lean Beef: Provides iron, zinc, and B vitamins, all of which are beneficial for muscle recovery and overall energy levels.
Fish and Seafood

- Salmon: Rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation and aid in recovery.
- Tuna: Packed with protein and also contains a range of vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins.
Plant-Based Proteins
For vegetarians and vegans, plant-based proteins offer excellent muscle-building potential:
- Lentils: High in protein, fibre, and iron, essential for oxygen transport to muscles.
- Chickpeas and Beans: Good sources of protein and slow-digesting carbs, providing a steady energy source.
- Tofu and Tempeh: Soy-based proteins that offer all essential amino acids for muscle repair.
High Protein Vegan Foods Ranked from Best to Worst
Dairy Products
- Greek Yoghurt: High in protein, particularly casein, which is slow-digesting and ideal for sustained muscle repair.
- Cottage Cheese: Provides a mix of fast- and slow-digesting proteins, making it a great option for muscle growth.
- Milk: Contains both whey and casein, making it effective for muscle recovery and growth when consumed post-workout.

Essential Carbohydrates for Muscle Fuel
Carbohydrates replenish glycogen stores and provide the energy needed for intense workouts. Aim for complex carbs that provide sustained energy.
Whole Grains
- Oats: High in fibre and slow-digesting, oats are ideal for providing long-lasting energy.
- Brown Rice: A staple for bodybuilders, brown rice provides carbs and fibre for sustained energy.
- Quinoa: Offers both carbs and protein, and is one of the few plant-based foods containing all essential amino acids.
Vegetables and Fruits
Vegetables and fruits not only offer carbs but also essential vitamins and antioxidants.
- Sweet Potatoes: Provide slow-release carbs, potassium, and antioxidants.
- Bananas: Rich in quick-release carbs, perfect for a pre- or post-workout snack.
- Berries: Packed with antioxidants that help reduce muscle inflammation and speed up recovery.
Healthy Fats for Hormone Support
Healthy fats play a key role in hormone regulation, including testosterone, which is essential for muscle growth. They also provide a concentrated energy source.
Nuts and Seeds

- Almonds: Contain healthy fats, protein, and magnesium, which aids in muscle function.
- Chia Seeds: High in omega-3s, fibre, and protein, making them ideal for muscle recovery.
- Walnuts: Another excellent source of omega-3s and protein.
Oils
- Olive Oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats, olive oil supports heart health and inflammation reduction.
- Coconut Oil: Provides medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) which can be quickly used for energy.
- Avocado: Full of healthy fats and fibre, avocado also provides potassium, which aids muscle contraction and function.
Food Labels That Sound Healthy But Are NOT
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel provide both protein and omega-3 fatty acids, reducing muscle soreness and improving recovery times.
Hydration: The Often Overlooked Factor in Muscle Gain

Staying hydrated is crucial for muscle health. Muscles are 75% water, and dehydration can impair performance, recovery, and growth. Aim for around 3 litres of water per day, more if you’re sweating heavily during workouts.
- Water: Essential for muscle function, nutrient transport, and toxin removal.
- Electrolytes: Include drinks or foods with sodium, potassium, and magnesium to maintain electrolyte balance, particularly after intense exercise.
How Much Should You Run Every Week to Lose Fat
Effective Timing and Frequency for Optimal Muscle Gain
While the “anabolic window” (30-60 minutes post-workout) isn’t as narrow as once thought, meal timing can still help maximise gains.
- Pre-Workout Nutrition: A balanced meal with carbs and protein about 2-3 hours before training can boost energy levels.
- Post-Workout Nutrition: Consuming protein and carbs post-workout helps muscle recovery and replenishes glycogen.
- Protein Spread: Aim to consume protein every 3-4 hours to maintain muscle protein synthesis throughout the day.
Supplements to Consider for Muscle Gain
While whole foods are always the best option, some supplements can provide added benefits.
Protein Powders
- Whey Protein: A fast-digesting protein that’s ideal for post-workout recovery.
- Casein Protein: A slow-digesting option that’s great for sustaining amino acid levels overnight.
- Plant-Based Protein: For those avoiding animal products, options like pea, hemp, or rice protein can also be effective.
Creatine
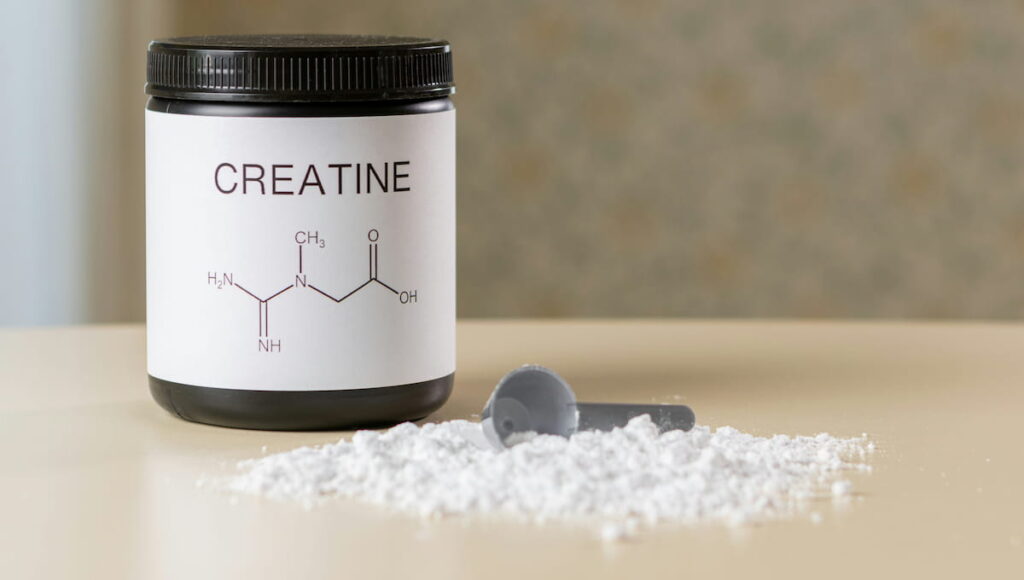

Creatine is one of the most researched supplements for muscle gain and strength. It helps replenish ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells, improving performance in high-intensity workouts.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) help reduce muscle breakdown during workouts. They are especially useful during fasted workouts or prolonged training sessions.
Omega-3 Supplements
If you don’t consume fatty fish regularly, an omega-3 supplement can help reduce inflammation and support muscle recovery.
Multivitamins and Minerals
Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals can slow down muscle recovery and reduce performance. A multivitamin can help cover any gaps, especially if you’re training intensely.
Sample Meal Plan for Muscle Gain

Here’s a basic meal plan to get an idea of how to structure your meals for muscle gain:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with whole-grain toast, avocado, and a side of berries.
- Mid-Morning Snack: Greek yoghurt with chia seeds and a banana.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast, quinoa, mixed greens, and roasted sweet potatoes.
- Afternoon Snack: Cottage cheese with almonds and an apple.
- Dinner: Salmon fillet with brown rice, steamed broccoli, and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Evening Snack: A protein shake with casein protein powder, or cottage cheese with a handful of nuts.
Conclusion
Achieving muscle gain requires a combination of strength training and proper nutrition. Focusing on high-quality proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats provides your muscles with the nutrients they need for growth and recovery. Remember that while supplements can aid your goals, whole foods should make up the bulk of your diet. Balancing meal timing and staying hydrated are equally important in supporting muscle gain. So, whether you’re new to strength training or an experienced lifter, eating the right foods consistently will set you on the path to building muscle effectively and sustainably.
Key Takeaways
| Nutritional Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein | Essential for muscle repair; include a variety of sources like meat, dairy, and legumes. |
| Carbohydrates | Provide energy for workouts and recovery; focus on complex carbs like oats and brown rice. |
| Healthy Fats | Support hormone production and energy; sources include nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. |
| Hydration | Critical for performance and recovery; aim for 3L daily with electrolytes as needed. |
| Supplements | Optional but helpful: consider whey protein, creatine, BCAAs, and omega-3s. |
| Meal Timing | Spread protein intake throughout the day; carbs post-workout are beneficial. |
References
- Phillips, S. M., & Van Loon, L. J. C. (2011). “Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to optimum adaptation.” Journal of Sports Sciences, 29(sup1), S29-S38.
- Jäger, R., et al. (2017). “International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), 20.
- Cribb, P. J., & Hayes, A. (2006). “Effects of supplement timing and resistance exercise on skeletal muscle hypertrophy.” Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 38(11), 1918-1925.
- Hulmi, J. J., Lockwood, C. M., & Stout, J. R. (2010). “Effect of protein/essential amino acids and resistance training on skeletal muscle hypertrophy: a case for whey protein.” Nutrition & Metabolism, 7(1), 51.
- Kreider, R. B., et al. (2017). “International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), 18.
image sources
- assorted nuts: studioM