Biohacking, often referred to as “DIY biology,” involves making small, incremental changes to your body and lifestyle to improve performance, health, and well-being. The term may bring to mind images of futuristic implants or extreme experiments, but in practice, biohacking can involve a range of simple strategies that enhance physical and mental resilience. In this article, we will explore how to biohack your body to be stronger through scientifically-backed methods, including nutrition, exercise, sleep optimisation, and the use of supplements and technology.
Table of Contents
The Fundamentals of Strength: Muscle Growth and Adaptation
Before diving into specific biohacking strategies, it’s essential to understand the basics of strength-building. Strength primarily revolves around your muscles’ ability to generate force, which relies on two processes: hypertrophy (muscle growth) and neuromuscular adaptation.
Muscle Hypertrophy
Muscle hypertrophy refers to the enlargement of muscle cells in response to resistance training. When muscles are placed under stress—such as during weight lifting—they experience tiny tears. Your body repairs these tears, leading to muscle growth. Protein synthesis, hormonal balance, and sufficient recovery play key roles in this process.
Neuromuscular Adaptation
Strength isn’t only about bigger muscles; it’s also about training the nervous system to communicate better with muscles. This is called neuromuscular adaptation. Regular training, particularly with progressive overload (gradually increasing resistance), helps improve this coordination, making muscles more efficient at producing force.
5 Steps to Build a Perfect Male Physique
Biohacking Techniques to Build Strength
1. Optimising Nutrition for Strength
Nutrition is the cornerstone of strength building. The right balance of macronutrients, micronutrients, and hydration can significantly impact muscle growth, recovery, and performance.
Protein Intake
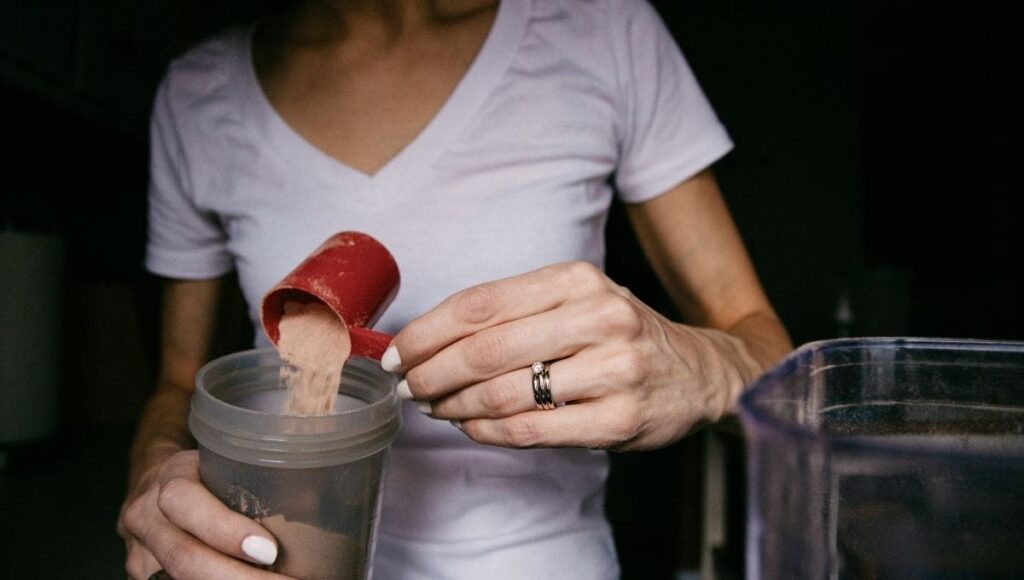

Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. The amino acids from dietary protein are the building blocks that help muscle tissue recover and grow after stress from exercise. To promote muscle growth, it’s commonly recommended to consume 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. This can be sourced from lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and protein supplements.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are crucial for energy, particularly during intense workouts. Glycogen, stored in muscles, is the primary fuel for resistance training. A diet too low in carbs can hinder performance and recovery. Athletes focusing on strength should aim for 3 to 5 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight daily.
The Most Attractive Male Body Type According to Women
Healthy Fats
Dietary fat is essential for hormone production, including testosterone, which plays a significant role in muscle growth. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, are linked to improved muscle recovery and reduced inflammation.
Supplements for Strength
Certain supplements have been scientifically shown to support muscle growth and strength:
- Creatine: This compound increases ATP production, offering more energy during short, intense efforts like lifting weights. Numerous studies have shown creatine to be one of the most effective supplements for enhancing muscle strength and size.
- Beta-alanine: This amino acid helps buffer lactic acid in muscles, reducing fatigue during high-intensity exercises.
- Whey protein: Quick-digesting and rich in essential amino acids, whey protein is a convenient way to meet your protein needs post-workout.

2. Strategic Exercise Selection
Building strength isn’t only about spending time in the gym; it’s about using that time wisely. Some forms of exercise are more effective for building strength than others.
Compound Movements
Compound movements, such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses, engage multiple muscle groups and joints simultaneously. These exercises are highly effective at building overall strength because they mimic real-world movement patterns and promote neuromuscular adaptation.
Progressive Overload
Strength training should follow the principle of progressive overload, meaning you gradually increase the weight, repetitions, or intensity of exercises over time. This constant challenge forces muscles and the nervous system to adapt, leading to greater strength gains.
5 Methods of Progressive Overload to Force Muscle Growth
Plyometric Training
Plyometric exercises, such as box jumps and explosive push-ups, focus on increasing muscle power, the ability to generate force quickly. These exercises strengthen the fast-twitch muscle fibres responsible for explosive movements, which are critical for strength-based sports.
3. Enhancing Recovery for Greater Strength
Recovery is a critical but often overlooked aspect of strength building. Muscles don’t grow during workouts; they grow during rest. Efficient recovery not only reduces the risk of injury but also ensures that muscles repair and adapt properly.
Sleep Optimisation

Sleep is arguably the most powerful recovery tool available. It’s during sleep that the body releases growth hormone and repairs damaged muscle tissue. Studies suggest that 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night is ideal for athletes and strength trainers. Lack of sleep impairs muscle recovery, cognitive function, and hormone regulation, making it harder to build strength.
Active Recovery
Incorporating low-intensity activities, such as light cycling or yoga, on rest days can promote blood flow to muscles without placing them under significant stress. This helps deliver nutrients to tissues and speeds up the removal of metabolic waste, supporting faster recovery.
Massage and Myofascial Release
Techniques like massage and foam rolling help reduce muscle tightness and improve flexibility, preventing injuries and improving recovery times. These techniques work by releasing tension in the fascia, the connective tissue surrounding muscles.
4. Biohacking Hormonal Health
Hormones, particularly testosterone and growth hormone, play a crucial role in muscle growth and strength. Hormonal imbalances can sabotage even the best training plans.
Natural Methods to Boost Testosterone
Testosterone is vital for muscle growth, bone strength, and energy levels. Here are some biohacks to naturally enhance testosterone production:
- Weight training: Studies show that strength training, particularly heavy lifting, can increase testosterone levels .
- Vitamin D: Deficiency in vitamin D has been linked to lower testosterone levels. Ensuring adequate sun exposure or supplementation can help optimise hormone levels.
- Zinc and magnesium: These two minerals are essential for testosterone production. They are often depleted by intense exercise, so supplementation may be beneficial.

Balancing Cortisol
Cortisol, the body’s stress hormone, can have a catabolic effect, meaning it breaks down muscle tissue. Chronic stress, whether from overtraining or lifestyle factors, leads to elevated cortisol levels, which can hinder strength gains. Meditation, adequate sleep, and proper nutrition are all effective in keeping cortisol levels in check.
The Most Attractive Female Body Type According to Men
5. Embracing Technology for Enhanced Strength
Advances in wearable technology, genetic testing, and recovery devices can give you data-driven insights into your body’s performance and recovery needs.
Wearable Devices
Wearable fitness trackers can monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, and training load. Some advanced models even track variables like heart rate variability (HRV), which can indicate recovery status and readiness for intense exercise. Biofeedback from these devices allows for more personalised and informed training decisions.
Cold Therapy and Cryotherapy
Cold therapy, including ice baths and cryotherapy, has gained popularity for its potential recovery benefits. Cold exposure reduces inflammation, helps alleviate muscle soreness, and may boost endorphin levels, improving mood and recovery after strenuous workouts.

Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
Electrical muscle stimulation involves sending small electrical impulses to muscles, causing them to contract. EMS is often used in rehabilitation but is also being adopted by strength athletes to enhance muscle recruitment and recovery.
6. The Role of Mindset and Mental Conditioning
The mind plays a crucial role in strength training. Techniques like visualisation, mindfulness, and mental resilience training can have tangible effects on performance.
Visualisation Techniques
Visualising success before a lift or competition can improve actual performance. This technique works by activating the same neural pathways used during physical performance. Research has shown that athletes who use visualisation perform better under pressure compared to those who don’t.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Mindfulness training can help athletes remain focused during training and competition. Managing mental stress through meditation or other relaxation techniques also reduces the impact of cortisol on muscle-building processes.

How to Make the Biggest Visual Change To Your Body Quickly
Conclusion
Biohacking your body to be stronger doesn’t require extreme measures. It’s about making strategic changes in your training, nutrition, recovery, and mindset that allow you to optimise your body’s natural processes. Whether through cutting-edge technology, tailored nutrition, or sleep optimisation, these biohacks, supported by science, offer actionable strategies to build strength effectively and sustainably.
By following these techniques, not only will you improve your physical strength, but you’ll also enhance your overall health and well-being. Remember that biohacking is highly individual, and what works for one person may need to be adjusted for another. Listening to your body, tracking progress, and making data-driven decisions are the key principles behind successful biohacking.
Key Takeaways
| Biohacking Strategy | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Nutrition | Prioritise protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats; consider supplements like creatine and beta-alanine. |
| Exercise | Focus on compound movements and progressive overload for maximum strength gains. |
| Recovery | Optimise sleep, use active recovery, and incorporate techniques like massage for faster recovery. |
| Hormonal Health | Support testosterone and balance cortisol through weight training, diet, and stress management. |
| Technology | Utilise wearable devices, cold therapy, and EMS for personalised training and recovery. |
| Mindset | Use visualisation and mindfulness to improve focus and performance in strength training. |
Bibliography
- Schoenfeld, B. J., 2010. “The Mechanisms of Muscle Hypertrophy and Their Application to Resistance Training.” Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 24(10), pp. 2857-2872.
- Phillips, S. M., 2014. “A Brief Review of Critical Processes in Exercise-Induced Muscular Hypertrophy.” Sports Medicine, 44(Suppl 1), pp. S71-S77.
- Kreider, R. B., et al., 2017. “International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), pp. 1-18.
- Cermak, N. M., et al., 2012. “Protein supplementation augments the adaptive response of skeletal muscle to resistance-type exercise training: a meta-analysis.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 96(6), pp. 1454-1464.
- Maughan, R. J., et al., 2018. “IOC consensus statement: dietary supplements and the high-performance athlete.” British Journal of Sports Medicine, 52(7), pp. 439-455.
image sources
- Rich Froning in Cold Plunge 2: Cold Plunge