If you’re aiming to enhance your push-up technique and increase the number of push-ups you can do, this video is tailored for you.
We’ll guide you through the proper execution of push-ups by addressing optimal body positioning, activating key muscles for stability, and introducing variations to unlock their full potential.
Following this tutorial by Jeremy Ethier, you can expect improved push-up performance, enhanced strength, and elevated muscle growth.
The Setup
Let’s start with the setup – a critical factor in refining your push-up form. Hand placement is key, forming an “arrow” shape when viewed from above. Lie down with your hands at mid-chest level, adjusting until your forearms align directly over your wrists and elbows form a 45 to 60-degree angle.
Most will find a hand placement just outside the shoulders at mid-chest level. Maintain this hand position as you transition onto your hands and knees, aligning your knees under your hips.
Activating the Muscles
Now, focus on activating muscles to stabilize your body, preventing energy leaks during push-ups. Push your knuckles into the floor, spreading your hands for optimal chest muscle engagement.
Slide your shoulders down to activate the lats and push the floor away, integrating the serratus anterior. Ensure your head is aligned with your body by pulling your chin back, reducing neck stress and positioning mid-back muscles for stabilization.
Attention to the Lower Body
With the upper body stabilized, shift attention to the lower body. Tuck your tailbone to set your hips in the right position. Take a breath, engage your core, and extend one leg back, followed by the other. Squeeze your thighs tightly for full leg extension. Now, you’re ready to execute the perfect push-up.
To perform the push-up, start by pulling yourself to the floor using back muscles, similar to a rowing motion.
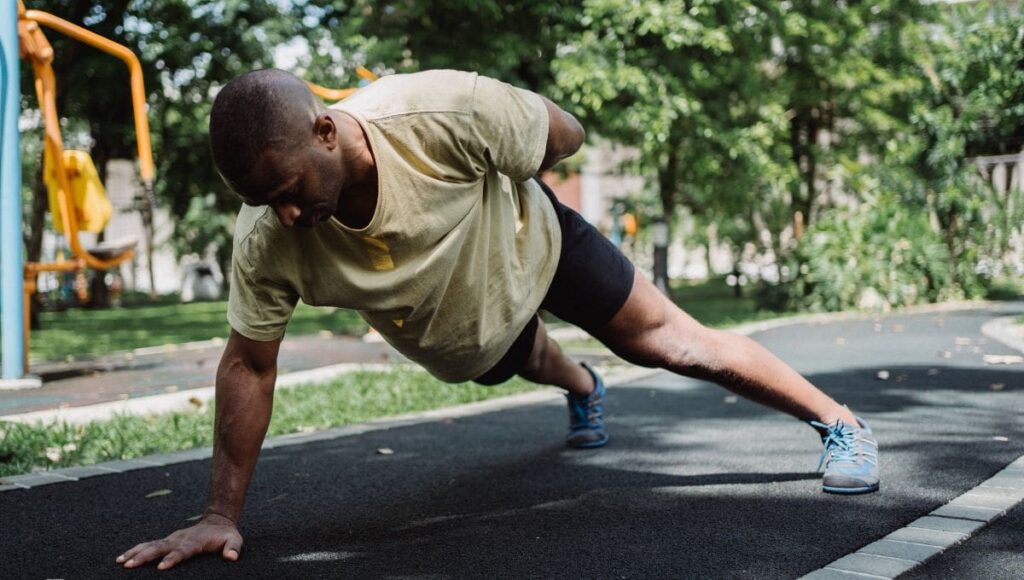

Maintain elbow alignment over wrists, allowing your body to move slightly forward. Squeeze your butt and thighs, pushing away from the floor to the top position, aligning head, hips, and feet in a straight line. Continue this form for subsequent reps.
Push Up Variations
Once you’ve mastered the standard push-up, consider appropriate variations based on your strength level.
For those struggling, try leg-banded push-ups or incline push-ups. If you’ve mastered standard push-ups, increase difficulty by slowing down reps or incorporating pauses at the bottom. Banded push-ups are a recommended advanced option.
Video
What are the Benefits of Push Ups?
Push-ups offer a variety of benefits for overall health and fitness. Here are some key advantages:
Strengthens Upper Body Muscles:
Push-ups primarily target the muscles in the chest, shoulders, and triceps. This helps in developing strength and definition in these areas.
Engages Core Muscles:
The plank-like position of a push-up engages the muscles in the core, including the abs and lower back. This helps improve overall core strength and stability.
Improves Endurance:
Performing push-ups regularly can enhance muscular endurance, allowing you to sustain physical effort for a more extended period.
Requires No Equipment:
Push-ups can be done anywhere, as they require no special equipment. This makes them a convenient and accessible exercise for individuals with varying fitness levels.
Enhances Functional Strength:
Push-ups simulate movements that are part of many daily activities, contributing to functional strength that can be applied in real-life situations.
Promotes Joint Health:
The controlled movement of push-ups helps in maintaining joint health by involving a range of motion in the shoulder and elbow joints.
Supports Cardiovascular Health:
As a compound exercise, push-ups can elevate your heart rate, contributing to cardiovascular health and improved circulation.
Facilitates Weight Management:
Regular engagement in physical activities like push-ups can aid in weight management by burning calories and promoting lean muscle mass.
Versatile Exercise:
Push-ups can be modified to suit various fitness levels and goals. Different hand placements and variations (e.g., incline or decline push-ups) allow for customization based on individual capabilities.
Improves Posture:
Proper execution of push-ups involves maintaining a straight body position, which can contribute to better posture by strengthening the muscles in the back.
Boosts Metabolism:
The intensity of push-ups can contribute to an increased metabolic rate, potentially aiding in weight loss and weight maintenance.
Cost-Effective Workout:
Since no special equipment is needed, push-ups offer a cost-effective way to incorporate strength training into your fitness routine.
Incorporating push-ups into a well-rounded exercise regimen can contribute to overall physical fitness and health. It’s important to perform push-ups with proper form to maximize their benefits and reduce the risk of injury. If you have any existing health concerns or conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program.
What Muscles Do Push Ups Develop?
Push-ups are a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, making them an effective and efficient strength-building workout. The primary muscles worked during push-ups include:
Pectoral Muscles (Chest):
The chest muscles are the primary movers during push-ups. As you push your body away from the floor, the pectoralis major and minor muscles contract.
Deltoid Muscles (Shoulders):
The anterior (front) part of the deltoid muscles is heavily involved in the lifting phase of a push-up. They contribute to the shoulder movement as you push up and away from the ground.
Triceps Brachii (Triceps):
The triceps, located at the back of the upper arm, are responsible for extending the elbow joint during the upward phase of the push-up.
Serratus Anterior:
This muscle is located on the sides of the ribcage and plays a crucial role in shoulder movement and stabilization. It is engaged as you protract your shoulder blades during a push-up.
Rectus Abdominis and Transverse Abdominis (Abdominals):
The core muscles, including the rectus abdominis and transverse abdominis, are engaged to maintain a straight body position throughout the push-up, contributing to core strength.
Obliques (Side Abdominal Muscles):
The oblique muscles, located on the sides of the abdomen, help stabilize the torso and prevent rotation during push-ups.
Quadriceps (Front Thigh Muscles):
The quadriceps are engaged during the straightening of the legs as you lift your body off the ground, contributing to lower body stability.
Scapular Stabilizers (Rhomboids, Trapezius):
Muscles in the upper back, such as the rhomboids and trapezius, are involved in stabilizing the scapulae (shoulder blades) during the movement.
Latissimus Dorsi (Lats):
The lats, located in the back, play a role in stabilizing the shoulders and upper body during push-ups.
Gluteus Maximus (Glutes):
The glutes, located in the buttocks, are engaged to maintain a straight body position and contribute to overall stability.
While these are the primary muscles targeted, push-ups also involve various stabilizing muscles throughout the body.
Proper form is essential to effectively engage these muscles and minimize the risk of injury. Additionally, different hand placements and variations of push-ups can shift the emphasis onto specific muscle groups.
Learn More
5 Reasons Why Walking for 30 Minutes Every Day will Help You Live a Longer Life
13 Easy to Cook Meals for Burning Your Visceral Fat Quicker (GET LEAN FAST)
8 Reasons Why Meal Prepping is Your Golden Ticket to a Flatter Stomach in 2024
Perfect 5 Minutes Posture Routine
How to Hack Muscle Growth in 2024
How to Get Stronger and Better Looking Glutes
The Perfect Biceps Workout for Muscle Mass and Great Looking Arms
image sources
- One arm push-up: Ketut Subiyanto on Pexels














